When to use Presente do Indicativo?
The present tense in Portuguese (Presente do Indicativo) is used to describe:
- Actions Happening Now*: it can describe actions happening right now with the present tense.
- Ele lê o jornal. (He reads the newspaper.)
- Nós assistimos a um filme. (We watch a movie.)
- Habitual Actions: it describes things you do regularly or as part of your routine.
- Eu estudo português todos os dias. (I study Portuguese every day.)
- Eles jogam futebol aos sábados. (They play soccer on Saturdays.)
- Facts and General Truths: it is used to talk about the things that are always true.
- O sol nasce no leste. (The sun rises in the east.)
- Moramos em uma grande cidade. (We live in a big city.)
- Near Future: It can sometimes refer to the near future, especially when paired with time expressions
- Amanhã, eu vou ao cinema. (Tomorrow, I’m going to the movies.)
- No verão, vamos para o Algarve. (In the summer, we go to the Algarve.)
*Portuguese often uses a construction with “estar a” (to be) + the infinitive to emphasize ongoing actions. For example: Agora estou a comer (Now I’m eating) ESTAR A + INFINITIVO / ESTAR + GERUNDIO
Verb conjugation in the present tense
Portuguese verb conjugation is quite regular. To conjugate a verb in Portuguese, the ending -ar/-er/-ir is truncated and the verb stem takes the following endings:
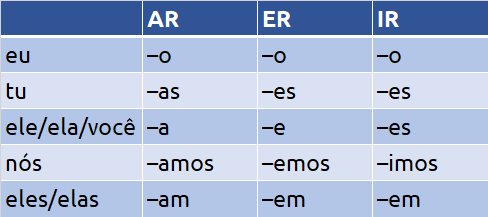
So, for example, the regular verbs falar (to speak), beber (to drink), and partir (to leave) have the following conjugations:

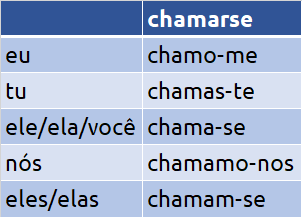
Reflexive Verbs in Portuguese
Reflexive verbs in Portuguese describe actions that the subject does to itself, like “acordar-se” (to wake up), “chamar-se” (to call). After the conjugation of the verb, they need a reflexive pronoun (me, te, se or nos) before or after the verb with a hyphen. When placed after the verb, the first person plural s is cut off from the stem.
Irregular Verbs in Portuguese
Portuguese has some irregular verbs. These verbs don’t follow the same conjugation patterns as regular verbs and require memorization. Some of the most common ones are shown below:
